Latest Findings: NMN Reverses Cognitive Impairment from Exposure to Common Environmental Pollutant
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) restores learning and memory in rats exposed to a common environmental pollutant found in laundry detergent — nonylphenol (NP).
Highlights
- NP exposure triggers learning and memory impairments in rats, however, NMN (the equivalent to 600 mg per day for humans) restores cognitive function.
- NMN likely rescues cognition by increasing the quantity of memory-associated receptors — serotonin receptors — in a learning and memory-related brain region, the hippocampus.
Banned in the European Union, the hazardous compound NP is an ingredient found in dishwashing and laundry detergents. High dosage exposure to NP can cause reproductive damage from stimulation of estrogen receptors, and accumulating evidence suggests it impairs cognition. It’s not well understood how much exposure to NP most people outside the European Union undergo. Furthermore, no current cognition-preserving remedies have been identified for those with high exposure.
Published in Food and Chemical Toxicology, Liu and colleagues from the South China Agricultural University show that NP exposure drives learning and memory impairments in rats but that low-dosage NMN restores cognition. NMN increases the quantity of learning associated receptors called serotonin receptors in a brain region with key roles in learning and memory, the hippocampus. These findings suggest that NMN can help prevent cognitive decline for those exposed to high levels of NP.
NMN Reverses Nonylphenol-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Restoring Serotonin Receptors
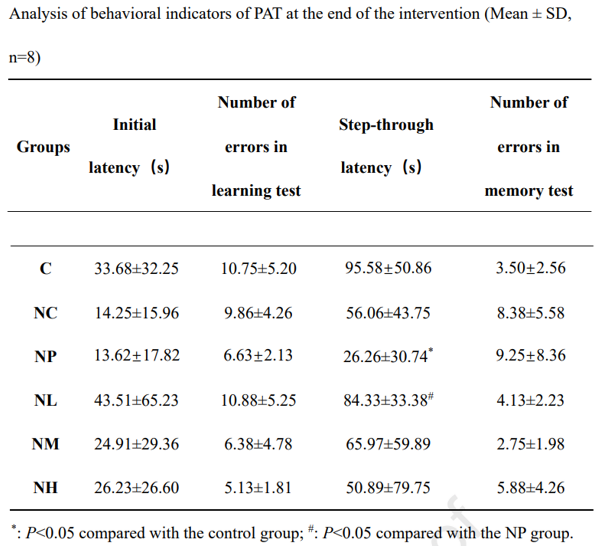
To test whether NMN can alleviate learning and memory impairments following NP exposure, Liu and colleagues measured cognition in NP exposed rats along with those also treated with NMN. Testing the rats’ cognitive function involved a passive avoidance test that takes advantage of rat proclivity to avoid lighted areas. The researchers placed the rats into a compartment with light where they had the option to relocate to a dark compartment. The catch for the rats was that they received a foot shock when trying to walk into the darkened compartment. Thus, the longer it took the rats to walk to the darkened compartment (step-through latency), the better their fear-based memory of the foot shock.
Interestingly, NP exposure drastically reduced the step-through latency, an indicator of impaired learning and memory. Adding low-dose NMN treatments to the NP exposure restored step-through latency durations, indicative of improved learning and memory. These findings suggest that taking NMN can help prevent cognitive impairments from NP exposure.
Liu and colleagues sought to find how NMN reverses learning and memory impairments in rats exposed to NP. They considered memory-associated receptors (serotonin receptors) in a brain region linked to learning and memory, the hippocampus. They measured serotonin levels in this brain region, finding that NP exposure significantly reduced serotonin receptor levels. Low-dose NMN treatment in addition to NP exposure restored levels of three types of serotonin receptors — 5-HTR1A, 5-HTR4 and 5-HTR6 — and medium and high NMN doses rescued the abundance of only one serotonin receptor type — 5-HTR1A. These findings provide evidence that low-dose NMN restores cognition by increasing the abundance of all three serotonin receptor types, while higher doses increase one serotonin receptor type. These results may help explain why low-dose NMN in addition to NP exposure significantly restored cognition, while higher NMN doses conferred a statistical trend, albeit non-significant, toward cognition restoration.
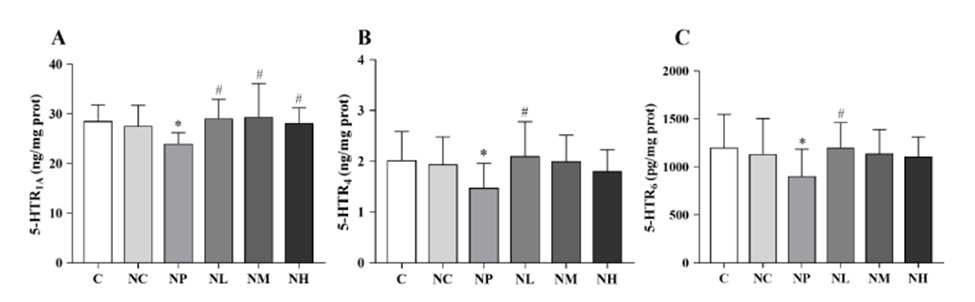
The Mechanism Behind NMN Restoring Serotonin Receptors Remains Uncertain
The study supports that low-dosage NMN can restore cognition following NP exposure, at least in rats. Furthermore, memory formation and retrieval associated serotonin receptor levels increased with low-dosage NMN treatments. These data beg the question of how NMN increases hippocampal serotonin receptor quantities.
The way NMN confers these benefits still remains largely unknown, but it may have something to do with sirtuin proteins. NMN increases levels of the essential pro-longevity molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Sirtuin proteins depend on NAD+ for their function, and with increased NAD+ from NMN treatments, sirtuins may activate certain proteins called transcription factors that regulate the activation of various genes. Along those lines, it’s possible that through sirtuins, NMN increases the activation of genes coding for serotonin receptors.
We still need more research to uncover NP-associated reproductive damage and cognition impairment in humans. In that light, NMN may help counter NP’s deleterious side effects, especially as they relate to cognitive function.
NMN can be obtained for between $40 and $80 for a month’s supply taken at 250 mg per day. The study’s low dosage treatment of 125 mg/kg was the most successful in restoring cognition. At the same time, 125 mg/kg per day is equivalent to about 600 mg per day for a human weighing 165 pounds, which isn’t necessarily considered low for humans. Thus, for the same cognition-preserving effects, humans may need to take around 500 mg or more of NMN per day.
Model: SD rats
Dosage: 270 mg/kg per day of nonylphenol for 28 days, 250 mg/kg per day for NMN negative control group, 125 mg/kg per day for low dose NMN group, 250 mg/kg per day for NMN medium dose group, and 500 mg/kg per day for high dose NMN group for 28 days

