NMN Reduces Weight, Cholesterol, and Blood Pressure in Overweight Adults: Harvard Study
In overweight or obese adults, NMN supplementation significantly reduces body weight, cholesterol, and diastolic blood pressure — when blood fills the heart.
Highlights:
- A Daily 2,000 mg dose of nicotinamide nucleotide (NMN) for 28 days cuts body weight in overweight or obese middle-aged and older adults.
- NMN also lowers total blood cholesterol, including low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, linked to blood vessel cholesterol buildup.
- Diastolic blood pressure is lowered by NMN, indicating that it can lower blood pressure.
Human studies have shown that NMN supplementation significantly increases blood NAD+ levels in overweight or obese adults. However, the physiological benefits of this increase have yielded mixed results.
Now, Harvard Medical School researchers show that, beyond weight loss, the MIB-626 formulation of NMN provides physiological benefits to overweight or obese adults. As reported in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, Bhasin and colleagues show that NMN decreases total cholesterol, including “bad” LDL cholesterol, and lowers blood pressure. These findings support the metabolic stabilizing effects of NMN, although further clinical trials with more participants and longer duration are needed for confirmation.
NMN Cuts Body Weight and Reduces Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
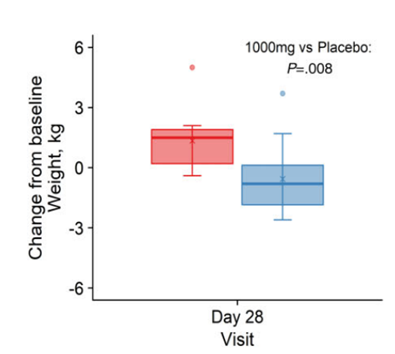
To investigate the impact of NMN on weight, Bhasin and colleagues administered two daily doses of 1,000 mg of NMN to middle-aged and older overweight or obese adults for 28 days. This led to more than a 6 lb. decrease in body weight when compared to participants who did not receive NMN for 28 days. This finding suggests that NMN supplementation promotes metabolic benefits, as evidenced by a substantial indicator of metabolic health, namely body weight.
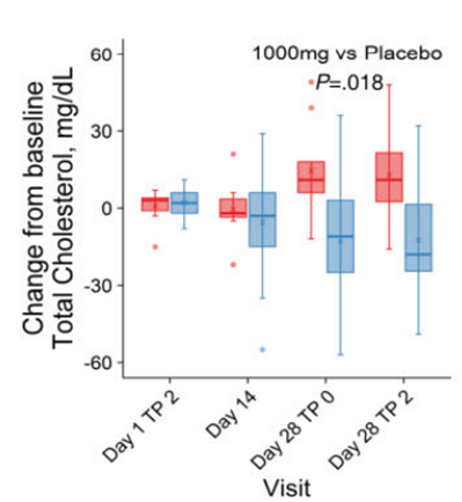
The researchers also assessed the effects of NMN on cardiovascular health by examining blood cholesterol levels. The results showed that NMN supplementation reduced both total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels, which are known to contribute to heart-related issues. These findings support the notion that NMN can positively impact the cardiovascular system by lowering cholesterol levels.
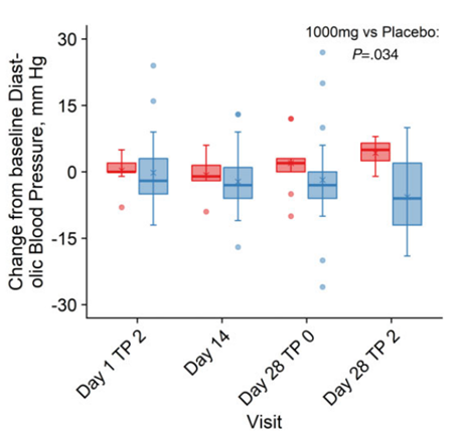
Furthermore, the study investigated whether NMN improves heart function by measuring diastolic and systolic blood pressure. Interestingly, NMN was found to specifically reduce diastolic blood pressure, which is a key factor in hypertension, while systolic blood pressure remained unaffected. These results suggest that NMN supplementation could be a potential strategy for alleviating hypertension in overweight and obese adults.
Could Longer Durations of NMN Supplementation Reverse Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction?
The study conducted by Bhasin and colleagues provides evidence that NMN can effectively reduce body weight in middle-aged and older overweight or obese adults. However, the relatively short duration of the study raises questions about the potential anti-obesity benefits that could be achieved with a longer dosing regimen. It is reasonable to assume that an extended study period may enhance the anti-obesity effects of NMN. Additionally, longer study durations could facilitate greater reductions in cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
It is important to note that the study had a limited number of participants (21 individuals) who received NMN. Although no effects on muscle strength or recovery time were observed in this study, conducting a future study with a larger sample size and longer duration could explore the possibility of NMN improving muscle performance when combined with a workout regimen.
In summary, the results of this study provide encouraging findings for overweight and obese adults seeking weight loss options and considering NMN supplementation. However, it is worth considering that the dosages utilized in this study (2,000 mg per day) were higher than those used in most other studies, making them relatively expensive, with a monthly cost exceeding $150.
Participants: Humans aged 45 years and older who are overweight or obese
Dosage: Two 500 mg MIB-626 NMN tablets twice daily (2 g total) for 28 days

