Japanese Study Indicates NMN Reverses Signs of Aging in Older Women
A new study finds that NMN improves the metabolism, hormone levels, and skin of postmenopausal women.
Highlights
- Supplementing older women with 300 mg of oral NMN improves sugar and cholesterol metabolism.
- NMN improves hormone levels as measured by the “mother hormone” – dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-s).
- Treatment with NMN reduces a process called glycation in the skin, suggesting the reversal of skin aging.
Studies using rodents have shown that supplementing with precursors of the essential molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) – improves numerous age-related health conditions. Whether humans can reap similar benefits from NAD+ precursors like nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) remains hotly contested.
Published in Glycative Stress Research, Yonei and colleagues from Doshisha University in Japan demonstrate that supplementing postmenopausal women with NMN improves markers of health that tend to decline with age, including metabolism and hormonal health. Moreover, NMN reduces the abundance of markers in the skin indicative of deteriorating skin health. These findings suggest that NMN may provide benefits to multiple physiological systems in the human body.
NMN Improves Metabolic, Hormonal, and Skin Health
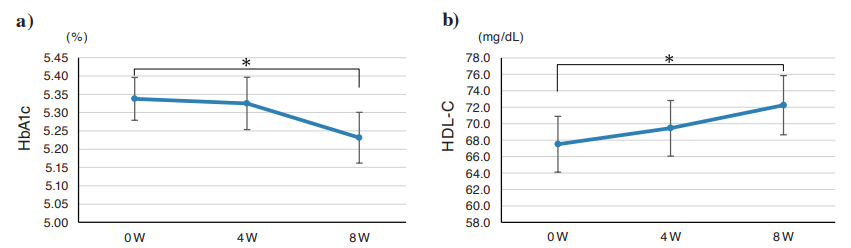
To better understand NMN’s effects on metabolism, the Japan-based research team measured HbA1c, an indicator of blood sugar levels commonly used to diagnose diabetes. HbA1c is a hemoglobin protein with a sugar attached. Increased HbA1c indicates higher blood sugar levels. After eight weeks of NMN treatment the researchers found that HbA1c significantly declined, suggesting improvements in sugar metabolism.What’s more, NMN increases levels of a type of cholesterol (high density lipoprotein c [HDL-C]) that picks up excess cholesterol and delivers it to the liver where it is broken down. Higher HDL-C levels in the blood are another key sign of improved metabolism.
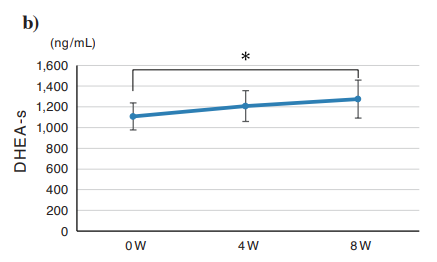
To then monitor NMN supplementation’s effects on hormonal health, Yonei and colleagues examined blood DHEA-s concentrations, the “mother hormone precursor” to sex hormones estrogen and testosterone. The research team found that eight weeks of NMN supplementation increase DHEA-s levels in the blood, which suggests an improvement in hormonal health.
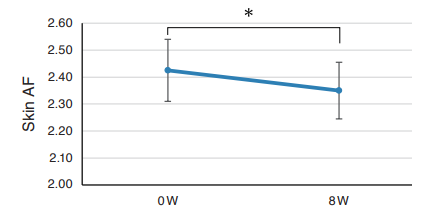
Sugars can react with proteins in a process called glycation, which has been linked to age-related diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Yonei and colleagues examined glycation levels by measuring advanced glycation end products [AGEs] with autofluorescence in the skin of participants. After taking NMN for eight weeks, the participants displayed a decrease in AGEs. Since increased levels of AGEs have been linked to advanced skin aging, the reduction in AGEs signaled that NMN confers benefits to aging skin.
The Study Supports that NMN Extends Number of Healthy Years Lived
Since other human NMN studies suggest differential effects on organ systems and tissues, such as in insulin sensitivity, muscle oxygen absorption, and overall physical performance, Yonei and colleagues’ results showing effects in multiple organ systems seems fitting. Indeed, Yonei and colleagues’ findings provide more evidence that NMN supplementation may improve metabolic, hormonal, and skin health. The positive changes in an array of markers representing multiple organ systems suggest that NMN may be a promising nutritional compound to possibly slow aging and extend the number of years lived in overall good health.
Model: Postmenopausal women between 50 and 80 years old
Dosage: 300 mg/day of NMN for eight weeks

