Longevity Supplement Ergothioneine Improves Sleep in New Study from Japan
For the first time, a longevity-associated antioxidant supplement, found in mushrooms, was revealed to improve sleep difficulties in humans.
Highlights
- Ergothioneine supplementation improves both subjective and objective measures of sleep.
- Ergothioneine supplementation increases anti-inflammatory and antioxidant molecules.
Adequate sleep is a fundamental aspect of healthy aging, as good sleep is associated with a 48% lower risk of all-cause mortality. Quality sleep improves cardiovascular health, memory consolidation, reproductive health, immunity, and mental health. On the other hand, inadequate sleep triggers the physiological processes that underlie biological aging, such as inflammation and oxidative stress.
Along those lines, it seems reasonable that both sleep and longevity (living longer) can be improved simultaneously by a compound that targets both inflammation and oxidative stress. While many compounds may fit this criterion, a recent study provides evidence that ergothioneine, a compound associated with countering cellular aging, can improve the sleep of middle-aged adults.
Ergothioneine Reduces Sleep Difficulty
The recent study, done by researchers at Suntory Global Innovation Center in Japan, included 92 participants (average age: ~53 years) with mild sleep complaints related to stress and anxiety. Every day for four weeks, half the participants took a placebo pill while the other half took a 20 mg ergothioneine supplement.
Based on a questionnaire called the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), it was found that ergothioneine supplementation reduced sleep difficulty. However, quality of sleep, sleep onset time, sleep duration, and sleep efficiency were reduced in both groups, suggesting ergothioneine had no effect on these latter parameters.
Ergothioneine Improves Objective Measures of Sleep
For a more objective assessment of sleep, the researchers had participants sleep for three consecutive days wearing an electroencephalogram (EEG), a cap with electrodes that measure brain wave activity. Our brainwaves change depending on whether we are awake or in which stage of sleep we are in. Thus, the EEG allows researchers to measure the sleep stages of study participants.
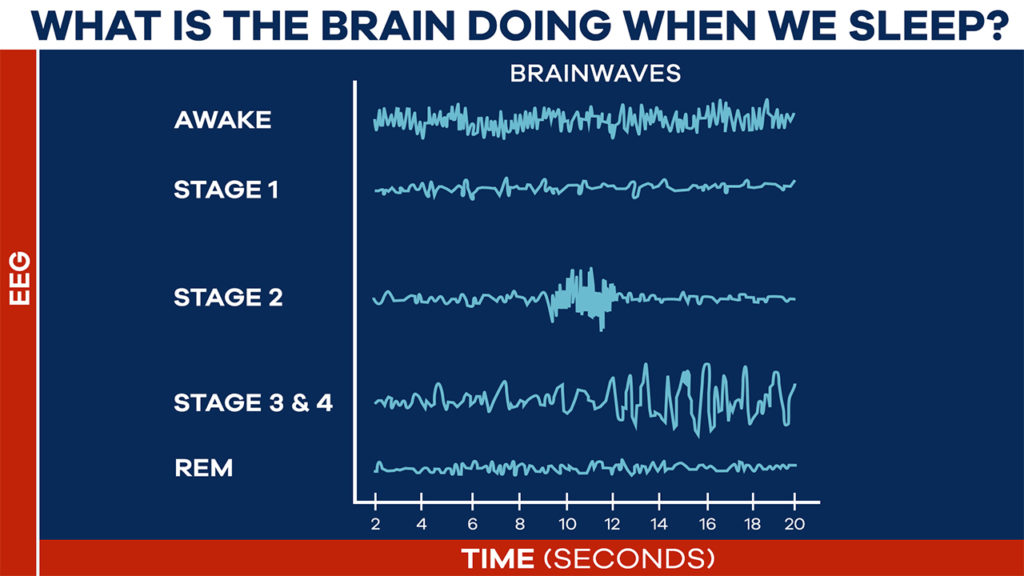
Remarkably, the results showed that ergothioneine reduced the duration of Stage 1 sleep, a state of drowsiness that lies between wakefulness and Stage 2 sleep. Furthermore, Stage 2 sleep, important for memory consolidation, was increased. Additionally, compared to baseline, the duration of REM sleep, also important for memory consolidation, was reduced in participants who took ergothioneine. The participants in the ergothioneine group also woke up fewer times after sleep onset, an indicator of improved sleep quality.
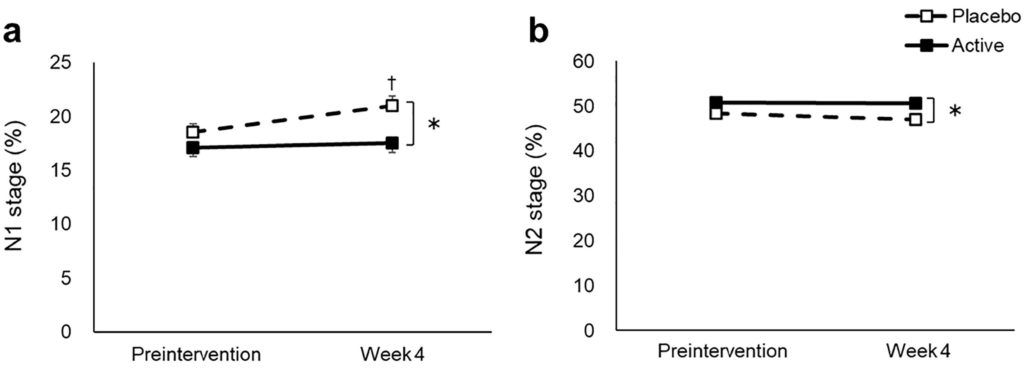
In the elderly, Stage 1 sleep increases at the expense of deeper levels of sleep. Similarly, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients exhibit an increase in Stage 1 sleep duration. The authors say,
“It is, therefore, further speculated that the sleep quality improvements elicited by ergothioneine may also serve to counteract changes associated with aging and the progression of AD.”
Still, it is unclear how reduced REM sleep duration is beneficial, a point not addressed by the authors of the study.
Ergothioneine Counters Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are metabolic byproducts that are responsible for oxidative stress. Oxidative stress — cellular damage — occurs if excessive levels of ROS go unchecked by antioxidants. In turn, oxidative stress can trigger inflammation, which further promotes cellular damage if chronically activated. Oxidative stress and inflammation increase in response to sleep deprivation, and both are underlying drivers of cellular aging.
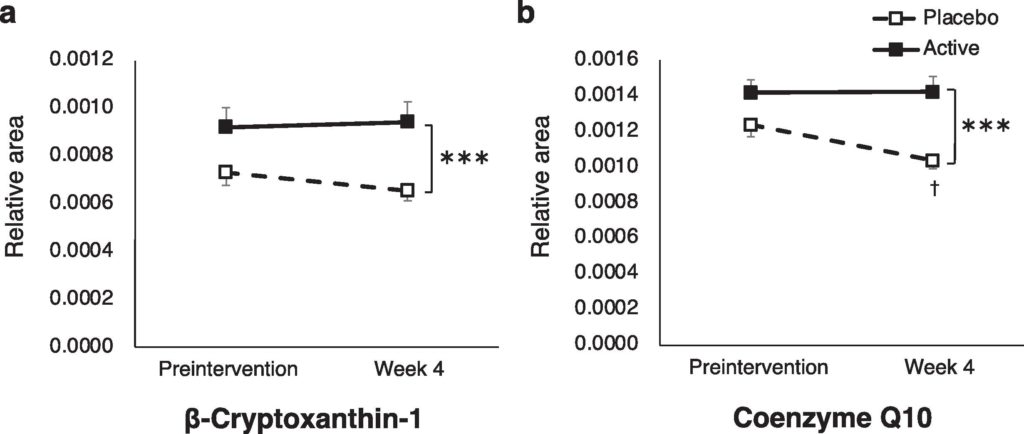
Importantly, the researchers found that supplementation with ergothioneine prevented a reduction in the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory molecules β-cryptoxanthin-1 and coenzyme Q10. These findings suggest that ergothioneine may improve both sleep and longevity by alleviating oxidative stress and inflammation.
Supplementing with Ergothioneine
Ergothioneine is most abundant in various mushroom species, but can also be found in foods like asparagus. However, to assure an adequate dose, supplementing with ergothioneine is likely the best option for most individuals. Based on this study, 20 mg of ergothioneine may be enough to improve sleep. The participants, who were healthy middle-aged adults, did not experience any serious side effects, suggesting ergothioneine supplementation is safe.
When it comes to longevity, ergothioneine has been shown to improve the memory of aged mice by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation. Moreover, ergothioneine has been shown to prolong the lifespan of mice by up to 21%. Interestingly, combining ergothioneine with the NAD+ precursor NMN was shown to improve cardiovascular health in sedentary aged mice. Furthermore, a study done on older adults suggests that 25 mg of ergothioneine can potentially improve cognition and sleep.
Considering the modest effects of 20 to 25 mg of ergothioneine on human subjects, it is possible that a higher dose is needed. However, more studies are necessary to determine if substantially higher doses of ergothioneine are safe and tolerable. Doses of up to 30 mg are available on the market.
Participants: Healthy middle-aged (average age: ~53 years) adults with sleep complaints
Dosage: 20 mg of ergothioneine for four weeks

